And How it Can Change Your Life in 30 Minutes.
By Gavin Seim (updated 01/13) – This may be the most important piece I’ve written on photographics. Because no matter what you photograph, once you see in Zones, you’ll never see the same again. You’re on your way to truly mastering light.
I started photographic study when I was twelve. But in recent years I’ve started working with 4×5 large format film and digital side by side. I’ve explored endless exercises in tonal control, “truly” learned to visualize, and implemented the Zone System that was developed by Ansel Adams and Fred Archer, both in my film and my digital work, in color and black and white. Zones are the language of light and they’ve changed everything about how I see.
Master Zones & Exposure Dynamics – Get Gavin’s Workshop Series.
The idea of visualizing and using Zones is not promoted much today. It seems much of the industry arrived at digital and decided that the past 150 years of photographic knowledge were somewhat irrelevant. Maybe it’s that many never took the time to understand Zones to begin with. Which is a shame because it’s so brilliant. What I’m about to show you is not taught much, but understanding it WILL change your image making forever. I’m not kidding; once you grasp this, you’ll never see light the same again. You’ll probably want more after this, so check out the links at the bottom for further reading. Also you can get hands on in my annual 3 day Lights & Shadows workshop. And check out my video series, EXposed which gets deep into Zones. OK lets dig in.
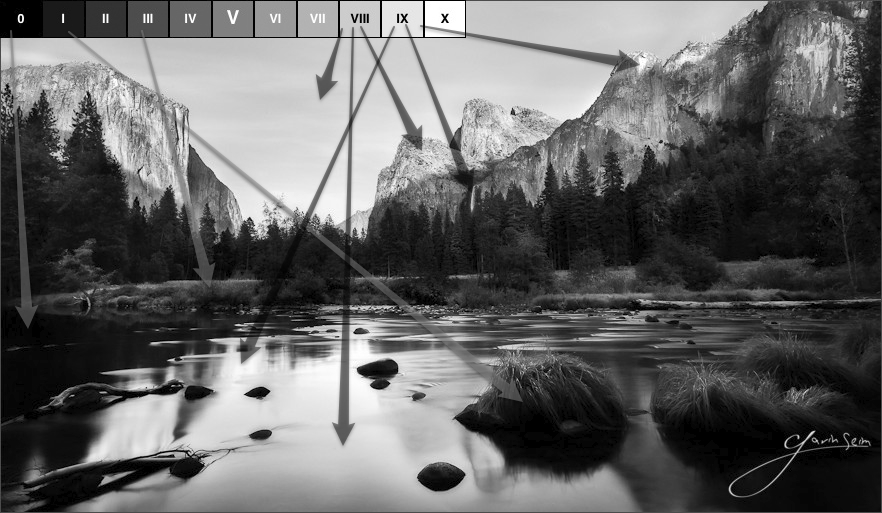
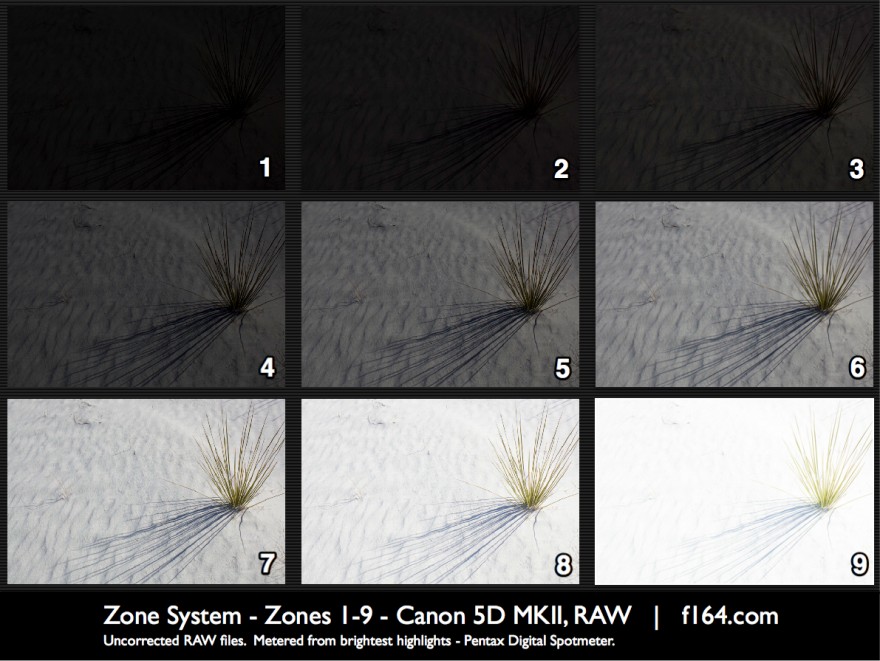
I’m going to stay simple because these concepts are simple. I’ve not come up with a new digital based zone system, a stripped down version, or an article filled with nerdy equations, white papers, or complex charts. This is not hard and you can start putting it to use TODAY. Since most of us are in the digital world, I’ll focus on that. I’m going to show you how to use the core of the Zone System to make you a vastly better photographer. I’ve also brought along some examples for analyzing said Zones.
To those of you who already know this, kudos. But I challenge you to consider whether you’re really using it, or just buzzing along in digital bliss and fixing things later. Excuse my bluntness, but this is happening to the best of us. We need to get back to basics and visualize, control tone, dynamic range, image quality and presentation
The Zone System was a complete approach that included everything from the initial exposure to the final print. Now we don’t use darkrooms much these days, so I’ll focus on the pivot point of the Zone System: the Zones themselves. That said, I would encourage you to study the whole process even if you don’t use film. It will help you gain a better understanding of photographics. Not only that, but old books like Fred Picker’s Zone VI workshop deal with it quickly and effectively and can often be had for mere pennies.
1. The Zone Scale.
The Zone Scale lies at the core of the Zone System. It consists of eleven squares that span from clipped black (Zone 0) to clipped white (Zone X). Each square represents a change of one stop. The first part of using Zones starts before you release the shutter. Truly visualizing your image is like nothing else. Once you master it, you see the image you plan to make (including your edits and refinements) in your mind before you ever take the photo. It changes how you photograph and how refined the resulting images become.

To begin with look at the Zone scale. Now look at your scene. Now back to me 😉 What’s outside your window right now? Visualize what Zones the things around you fall within. Then imagine you’re taking a photo. Imagine where the Zones “would” fall if the image came out exactly as you wanted. It does not have to be what you “see” but what you “visualize” for the finished image. How do YOU want to make it?
Think about how Zone levels on various objects in this scene would complement your primary subject as well as your supporting cast of elements. Sometimes it helps to begin by visualizing a scene in black and white even if your final image is going to be color. Thinking in terms of tones can be helpful, especially early in the process.






